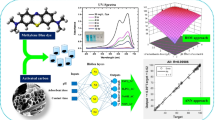
Abstract
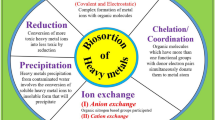
Water resources around the world are getting polluted day by day due to the rapidly developing industry. Industrial wastes have caused serious damage to the environment in recent years. Especially, dyes are waste products that mix with waters such as lakes, rivers and seas and have toxic and carcinogenic effects. In this study, the removal of methyl orange (MO) dye, which was chosen as a model dye compound, from aqueous solution by biosorption using hemp waste was investigated. The biosorption process was optimized by the parameters of pH, initial dye concentration and amount of biosorbent. Biosorption of MO to hemp waste was investigated by isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. It was determined that the biosorption equilibrium fitted to the Langmuir isotherm (\({R}^{2}\)=0.9739). As a result of the experimental studies, 83% biosorption value and 1428 mg/g maximum biosorption capacity were reached with 250 mg/L dye concentration and 0.5 g/L biosorbent amount at pH = 2. It was determined that the reaction kinetics were in accordance with the pseudo-second-order kinetics (\({R}^{2}\)=0.9911). In addition to, the study aims to evaluate to what extent the modeling of the biosorption process is successful. For this purpose, we used multigene genetic programming (MGGP), which has been renewed with the latest developments in the field of model extraction. The results show that MGGP is efficient for modeling the biosorption process in real environments. The analysis of MGGP models also showed that pH is the most important parameter affecting the biosorption process.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham RE, Wong CS, Puri M (2016) Enrichment of cellulosic waste hemp (Cannabis sativa) hurd into non-toxic microfibres. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA9070562
Ahmaruzzaman M (2012) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using activated papaya leaf. Sep Sci Technol 47(16):2381–2390. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2012.671432
Arici TA (2021) CTAB/H2O2 modified biosorbent for anionic dye from aqueous solutions: biosorption parameters and mechanism. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01920-0
Ashofteh PS, Haddad OB, Loáiciga HA (2015) Evaluation of climatic-change impacts on multiobjective reservoir operation with multiobjective genetic programming. J Water Resour Plan 141(11):04015030. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)wr.1943-5452.0000540
Assassi M, Madjene F, Harchouche S, Boulfiza H (2021) Photocatalytic treatment of crystal violet in aqueous solution: Box-Behnken optimization and degradation mechanism. Environ Prog Sustain Energ 40(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13702
Azeez RA, Al-zuhairi FKI (2021) Biosorption of dye by immobilized yeast cells on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles. Alex Eng J 61(7):5213–5222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.10.044
Bayazit ŞS (2014) Magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotubes for methyl orange removal from aqueous solutions : equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sep Sci Technol 49(9):1389–1400. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.879595
Berni R, Mandlik R, Hausman JF, Guerriero G (2021) Silicon-induced mitigatory effects in salt-stressed hemp leaves. Physiol Plant 171(4):476–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13097
Chimeni DY, Hirschberg V, Dubois C, Rodrigue D (2018) Rheological behavior of composites made from linear medium-density polyethylene and hemp fibers treated by surface-initiated catalytic polymerization. Rheol Acta 57(6):445–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-018-1089-5
Cramer NL (1985) In Proceedings of the 1st international conference on genetic algorithms. L. Erlbaum Associates Inc, USA. https://doi.org/10.5555/645511.657085
Dai D, Fan M (2010) Characteristic and performance of elementary hemp fibre. Mater Sci Appl 01(06):336–342. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2010.16049
Darwish AAA, Rashad M, AL-Aoh HA, (2019) Methyl orange adsorption comparison on nanoparticles: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigm 160:563–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.08.045
Dinçel NGK (2022) Determination of oil ratio and fatty acid composition of the seed obtained from the cannabis plant grown in Sivas ecological conditions in the first production year. J Erciyes Agric Anim Sci. https://doi.org/10.55257/ethabd.1081704
Fallahpour A, Olugu EU, Musa SN, Khezrimotlagh D, Wong KY (2016) An integrated model for green supplier selection under fuzzy environment: application of data envelopment analysis and genetic programming approach. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):707–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1890-3
Feli M, Abdali-Mohammadi F (2019) A novel recursive backtracking genetic programming-based algorithm for 12-lead ECG compression. SIViP 13(5):1029–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01441-4
Ferreira, C. Complex Systems 13, 2 (2001). arXiv preprint cs/0102027.
Gan Z, Chow TWS, Chau WN (2009) Clone selection programming and its application to symbolic regression. Expert Syst Appl 36:3996–4005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.02.030
Joudi M, Nasserlah H, Mouldar J, Hatimi B, El Mhammedi MA, Bakasse M (2020) Synthesis of an efficient hydroxyapatite – chitosan – montmorillonite thin film for the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes : adsorption isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. SN Applied Sci 2(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2848-3
Karaboğa, D (2017) Yapay Zeka Optimizasyon Algoritmalari. Nobel Akademi Yayıncılık.
Keshavarz A, Mehramiri M (2015) New Gene Expression Programming models for normalized shear modulus and damping ratio of sands. Eng Appl Artif Intell 45:464–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2015.07.022
Khwannimit D, Maungchang R, Rattanakit P (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea flower: an efficient catalyst for removal of methyl orange. J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1793974
Koza JR (1994) Genetic programming as a means for programming computers by natural selection. Stat Comput 4(2):87–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175355
Lafi R, Abdellaoui L, Montasser I, Hafiane A (2020) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution onto modified extracted cellulose from Stipa Tenacissima L. J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1845663
Li X, Wang G, Li W, Wang P, Su C (2015) Adsorption of acid and basic dyes by sludge-based activated carbon: isotherm and kinetic studies. J Cent South Univ 22:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2500-3
Li H, Wong, ML (2015) Financial fraud detection by using grammar-based multi-objective genetic programming with ensemble learning. In: 2015 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, CEC 2015-proceedings 1113–1120. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2015.7257014
Liu J, Wang X (2013) Novel silica-based hybrid adsorbents: Lead(II) adsorption isotherms. Sci World J 2013:897159. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/897159
Liu L, Shao L, Li X, Lu K (2016) Learning spatio-temporal representations for action recognition: a genetic programming approach. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(1):158–170. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2399172
Madjene F, Chergui A, Trari M (2016) Biosorption of Ni(II) by fig male: optimization and modeling using a full factorial design. Water Environ Res 88(6):540–547. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143016x14504669768859
Magdy YM, Altaher H, ElQada E (2018) Removal of three nitrophenols from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto char ash: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Appl Water Sci 8(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0666-1
Mahmoodi NM, Chamani H, Kariminia HR (2016) Functionalized copper oxide–zinc oxide nanocomposite: synthesis and genetic programming model of dye adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 57(40):18755–18769. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1094677
Moraglio A, Krawiec K, Johnson CG (2012) Geometric semantic genetic programming. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 7491 LNCS (PART 1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32937-1_3
Muduli PK, Das SK (2014) CPT-based seismic liquefaction potential evaluation using multi-gene genetic programming approach. Indian Geotech J 44(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-013-0048-4
Muduli PK, Das MR, Das SK, Senapati S (2015) Lateral load capacity of piles in clay using genetic programming and multivariate adaptive regression spline. Indian Geotech J 45(3):349–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-014-0142-2
Nguyen DTC, Van TT (2022) A chemometric approach based on Box-Behnken and response surface methodology for design and optimization of ciprofloxacin adsorption from water. Chem Pap 76(8):4873–4883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02207-y
Nguyen S, Mei Y, Zhang M (2017) Genetic programming for production scheduling: a survey with a unified framework. Complex Intell Syst 3(1):41–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-017-0036-x
Okpara OG, Ogbeide OM, Ike OC, Menechukwu KC, Ejike EC (2021) Optimum isotherm by linear and nonlinear regression methods for lead (II) ions adsorption from aqueous solutions using synthesized coconut shell–activated carbon (SCSAC). Toxin Rev 40(4):901–914. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2020.1802596
Pan I, Pandey DS, Das S (2013) Global solar irradiation prediction using a multi-gene genetic programming approach. J Renew Sust Energ Rev. DOI 10(1063/1):4850495
Poli R, Langdon WB, McPhee NF (2008) A Field Guide to Genetic Programing. In Wyvern (Issue March). http://www.essex.ac.uk/wyvern/2008-04/Wyvern April 08 7126.pdf
Riaz Q, Ahmed M, Zafar MN, Zubair M, Nazar MF, Sumrra SH, Ahmad I, Hosseini-Bandegharaeic A (2022) NiO nanoparticles for enhanced removal of methyl orange: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamic and desorption studies. J Environ Anal Chem 102:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1715383
Runjavec ŠM, Domanovac MV, Meštrović E (2022) Removal of organic pollutants from real pharmaceutical industrial wastewater with environmentally friendly processes. Chem Pap 76(3):1423–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01919-x
Searson DP, Leahy DE, Willis MJ (2010) GPTIPS:An open source genetic programming toolbox for multigene symbolic regression. In: Proceedings of the international multiconference of engineers and computer scientists IMECS, December, pp 77–80.
Sriram G, Bendre A, Altalhi T, Jung H, Hegde G (2022) Surface engineering of silica based materials with Ni–Fe layered double hydroxide for the efficient removal of methyl orange : Isotherms, kinetics, mechanism and high selectivity studies. Chemosphere 287:131976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131976
Su Y, Jiao Y, Dou C, Han R (2014) Biosorption of methyl orange from aqueous solutions using cationic surfactant-modified wheat straw in batch mode. Desalin Water Treat 52(31–33):6145–6155. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.811121
Subbaiah MV, Kim DS (2016) Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution by aminated pumpkin seed powder: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.016
Suganuma M, Shirakawa S, Nagao T (2018) A genetic programming approach to designing convolutional neural network architectures. IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/755
Tofan L, Paduraru C, Toma O (2016) Zinc remediation of aqueous solutions by natural hemp fibers: Batch desorption/regeneration study. Desalin Water Treat 57(27):12644–12652. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1052566
Viscusi G, Barra G, Verdolotti L, Galzerano B, Viscardi M, Gorrasi G (2019) Natural fiber reinforced inorganic foam composites from short hemp bast fibers obtained by mechanical decortation of unretted stems from the wastes of hemp cultivations. Mater Today Proc 34:176–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.672
Wu L, Liu X, Lv G, Zhu R, Tian L, Liu M, Li Y, Rao W, Liu T, Liao L (2021) Study on the adsorption properties of methyl orange by natural one-dimensional nano-mineral materials with different structures. Sci Rep 11(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90235-1
Zhu J, Yi J, Kang Q, Huang J, Cui Y, Zhang G, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zheng Z, Lu J, Hao L (2021) Anti-fatigue activity of hemp leaves water extract and the related biochemical changes in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 150:112054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112054
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kütük, N., Arslan, S. Biosorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution with hemp waste, investigation of isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies and modeling using multigene genetic programming. Chem. Pap. 76, 7357–7372 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02411-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02411-w