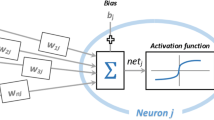
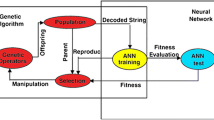
Abstract
Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of rocks is the most commonly used parameter in geo-engineering application. However, this parameter is hard for measurement due to a time consuming and requires expensive equipment. Therefore, obtaining this value indirectly using non-destructive testing methods has been a frequently preferred method for a long time. In order to obtain multiple regression models, input parameters need many assumptions. Thus, the estimation of the mechanical properties of rocks using by machine learning methods has been investigated. In this study, UCS values of rocks were estimated by reformulating with artificial intelligence-based age-layered population structure genetic programming (ALPS-GP) which is one of machine learning methods. Artificial neural network (ANN) and ALPS-GP models were performed to predict UCS from porosity, Schmidt hammer hardness and ultrasonic wave velocity test methods. For this purpose, the mentioned three tests (porosity, Schmidt hammer hardness and P-wave velocity) were carried out on ten different stones from Turkey. ANN was performed to evaluate this new technique. Reliability of UCS values determined by models was checked with mean absolute error (MAE), coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error (RMSE) and variance account for (VAF) values. These values were calculated as 1.64, 0.98, 2.11 and 99.81 for ANN, and 2.11, 0.98, 2.50 and 97.86 for ALPS-GP, respectively. It was observed that both methods used were quite successful in UCS estimation. The most important advantage of the ALPS-GP model is providing an equation for UCS estimation. In the light of the obtained findings, it has been revealed that this equation derived from ALPS-GP can be used in UCS estimation processes of similar rock types (limestone, dolomite and onyx).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khandelwal, M.; Ranjith, P.G.: Correlating index properties of rocks with P-wave measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 71, 1–5 (2010)
Sharma, P.K.; Singh, T.N.: A correlation between P-wave velocity, impact strength index, slake durability index and uniaxial compressive strength. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 67, 17–22 (2008)
Deere, D.U.; Miller, R.P.: Engineering classification and index properties of intact rock. Tech rep no. AFWL-TR 65-116. Univ Illinois: 300 (1966)
Singh, R.N.; Hassani, F.P.; Elkington, P.A.S.: The application of strength and deformation index testing to the stability assessment of coal measures excavations. In: Proc 24th US Symp rock Mech, Texas, AEG. Balkema, Rotterdam, 599–609 (1983)
Sheorey, P.R.; Barat, D.; Das, M.N.; Mukherjee, K.P.; Singh, B.: Schmidt hammer rebound data for estimation of large scale in situ coal strength. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 21, 39–42 (1984)
Haramy, K.Y.; De Marco, M.J.: Use of Schmidt hammer for rock and coal testing. In: Proc 26th US Symp rock Mech, 26–28 June, Rapid City, SD. Balkema, Rotterdam, 549–555 (1985)
Ghose, A.K.; Chakraborti, S.: Empirical strength indices of Indian coals: an investigation. Proceedings 27th US Symposium on Rock Mechanics, Rotterdam: Balkema, 59–61 (1986)
O'Rourke, J.E.: Rock index properties for geoengineering, underground development. Minerals Engineering 106–110 (1989)
Gokceoglu, C.: Schmidt sertlik çekici kullanılarak tahmin edilen tek eksenli sıkışma dayanımı verilerinin güvenilirliği üzerine bir değerlendirme. Jeoloji Mühendisliği 48, 78–81 (1996)
Katz, O.; Reches, Z.; Roegiers, J.C.: Evaluation of mechanical rock properties using a Schmidt hammer. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 37, 723–728 (2000)
Kahraman, S.: Evaluation of simple methods for assessing the uniaxial compressive strength of rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 38, 981–994 (2001)
Yilmaz, I.; Sendir, H.: Correlation of Schmidt hardness with unconfined compressive strength and Young’s modulus in gypsum from Sivas (Turkey). Eng. Geol. 66, 211–219 (2002)
Basarir, H.; Kumral, M.; Ozsan, A.: Predicting uniaxial compressive strength of rocks from simple test methods. Rockmec′2004-VIIth Regional Rock Mechanics Symposium. Sivas, Turkey (2004)
Kılıc, A.; Teymen, A.: Determination of mechanical properties of rocks using simple methods. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 67, 237–244 (2008)
Torabi, S.R.; Ataei, M.; Javanshir, M.: Application of Schmidt rebound number for estimating rock strength under specific geological conditions. J. Mining Environ. 1(2), 1–8 (2010)
Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.; Armaghani, D.J.; Mohd Amin, M.F.M.: Prediction of unconfined compressive strength of limestone rock samples using L-type Schmidt hammer. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 18(1), 1767–1775 (2013)
Inoue, M.; Ohomi, M.: Relation between uniaxial compres-sive strength and elastic wave velocity of soft rock.Proc., Int. Symp.on Weak Rock, Tokyo, Japan, Balkema, Rotterdam, 9–13 (1981)
Starzec, P.: Dynamic elastic properties of crystalline rocks fromsouth-west Sweden. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 362, 265–272 (1999)
Moradian, Z.A.; Behnia, M.: Predicting the uniaxial compressive strength and static Young’s modulus of ıntact sedimentary rocks using the ultrasonic test. Int. J. Geomech. 9(1), 14–19 (2009)
Kahraman, S.: A correlation between P-wave velocity, number of joints and Schmidt hammer rebound number. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 38, 729–733 (2001)
Yasar, E.; Erdogan, Y.: Correlating sound velocity with the density, compressive strength and Young’s modulus of carbonate rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 415, 871–875 (2004)
Chary, K.B.; Sarma, L.P.; Lakshmi, K.J.P.; et al.: Evaluation of engineering properties of rock using ultrasonic pulse velocity and uniaxial compressive strength, Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation 7–9 Dec. 379–385 (2006)
Khandelwal, M.: Correlating P-wave velocity with the physico-mechanical properties of different rocks. Pure Appl. Geophys. 170(4), 507–514 (2013)
Nourani, M.H.; Moghadder, T.M.; Safari, M.: Classification and assessment of rock mass parameters in Choghart iron mine using P-wave velocity. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 9(2), 318–328 (2017)
Mishra, D.A.; Basu, A.: Estimation of uniaxial compressive strength of rock materials by index tests using regression analysis and fuzzy inference system. Eng. Geol. 160, 54–68 (2013)
Yesiloglu-Gultekin, N.; Sezer, E.A.; Gokceoglu, C.; Bayhan, H.: An application of adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system for estimating the uniaxial compressive strength of certain granitic rocks from their mineral contents. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(3), 921–928 (2013)
Dehghan, S.; Sattari, G.; Chelgani, S.C.; Aliabadi, M.: Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity for Travertine samples using regression and artificial neural networks. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 20, 41–46 (2010)
Majdi, A.; Rezaei, M.: Prediction of unconfined compressive strength of rock surrounding a roadway using artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 23, 381–389 (2013)
Ceryan, N.; Okkan, U.; Samui, P.; Ceryan, S.: Modeling of tensile strength of rocks materials based on support vector machines approaches. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 37(16), 2655–2670 (2012)
Ceryan, N.: Application of support vector machines and relevance vector machines in predicting uniaxial compressive strength of volcanic rocks. J. Afr. Earth Sc. 100, 634–644 (2014)
Liu, Z.; Shao, J.; Xu, W., et al.: Indirect estimation of unconfined compressive strength of carbonate rocks using extreme learning machine. Acta Geotech. 10, 651–663 (2015)
Singh, R.; Vishal, V.; Singh, T.N.; Ranjith, P.G.: A comparative study of generalized regression neural network approach and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems for prediction of unconfined compressive strength of rocks. Neural Comput. Appl. 23, 499–506 (2013)
Mishra, D.; Srigyan, M.; Basu, A.; Rokade, P.: Soft computing methods for estimating the uniaxial compressive strength of intact rock from index tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 100, 418–424 (2015)
Mohamad, E.T.; Armaghani, D.J.; Momeni, E., et al.: Prediction of the unconfined compressive strength of soft rocks: a PSO-based ANN approach. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 74, 745–757 (2015)
Momeni, E.; Armaghani, D.J.; Hajihassani, M.; Amin, M.F.M.: Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of rock samples using hybrid particle swarm optimization-based artificial neural networks. Measurement 60, 50–63 (2015)
Mahdiyar, A.; Armaghani, D.J.; Marto, A., et al.: Rock tensile strength prediction using empirical and soft computing approaches. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 78, 4519–4531 (2019)
Asheghi, R.; Shahri, A.A.; Zak, M.K.: Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of different quarried rocks using metaheuristic algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 8645–8659 (2019)
Ceryan, N.; Okkan, U.; Kesimal.: A. Application of Generalized Regression Neural Networks in Predicting the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Carbonate Rocks. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 45, 1055–1072 (2012)
Celik, S.B.: Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of carbonate rocks from nondestructive tests using multivariate regression and LS-SVM methods. Arab. J. Geosci. 12(6), 193 (2019)
Acar, M.C.; Kaya, B.: Models to estimate the elastic modulus of weak rocks based on least square support vector machine. Arab. J. Geosci. 13(14), 590 (2020)
Shahri, A.A.; Asheghi, R.; Khorsand, M.Z.: A hybridized intelligence model to improve the predictability level of strength index parameters of rocks. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 3841–3854 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05223-9
Shahri, A.A.; Moud, F.M.; Lialestani, S.M.: A hybrid computing model to predict rock strength index properties using support vector regression. Eng. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01078-9
Koza, J.R.: Genetic Programming: On the Programming of Computers By Means of Natural Selection, 6th edn. MIT Press, London (1992)
Holland, J.H.: Application of natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor (1975)
Wang, C.; Ma, G.W.; Zhao, J.; Soh, C.K.: Identification of dynamic rock properties using a genetic algorithm. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41(1), 490–495 (2004)
Majdi, A.; Beiki, M.: Evolving neural network using a genetic algorithm for predicting the deformation modulus of rock masses. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 47, 246–253 (2010)
Ferreira, C.: Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Syst. 13(2), 87–129 (2001)
Baykasoğlu, A.; Güllü, H.; Çanakçı, H.; Özbakır, L.: Prediction of compressive and tensile strength of limestone via genetic programming. Expert Syst. Appl. 35, 111–123 (2008)
Shuhua, Z.; Qian, G.; Jianguo, S.: Genetic programming approach for predicting surface subsidence induced by mining. J. China Univ. Geosci. 17(4), 361–366 (2006)
Li, W.X.; Dai, L.F.; Houa, X.B.; Lei, W.: Fuzzy genetic programming method for analysis of ground movements due to underground mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 44, 954–961 (2007)
Çanakcı, H.; Baykasoğlu, A.; Güllü, H.: Prediction of compressive and tensile strength of Gaziantep basalts via neural networks and gene expression programming. Neural Comput. Appl. 18, 1031–1041 (2009)
Ozbek, A.; Unsal, M.; Dikec, A.: Estimating uniaxial compressive strength of rocks using genetic expression programming. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 5, 325–329 (2013)
Dindarloo, S.R.; Siami-Irdemoosa, E.: Estimating the unconfined compressive strength of carbonate rocks using gene expression programming. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 135(3), 309–316 (2015)
Behnia, D.; Behnia, M.; Shahriar, K.; Goshtasbi, K.: A New predictive model for rock strength parameters utilizing GEP method. Procedia Engineering 191, 591–599 (2017)
TSE 699: Tabii yapı taşları-muayene ve deney metodları, TSE Publication, Ankara (2009) [in Turkish].
ISRM: Suggested methods for determination of the Schmidt rebound hardness. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. & Geomech. Abstracts 15(3), 101–102 (1978)
ISRM: Suggested method for determining sound velocity. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. & Geomech. Abstracts 15(2), 53–58 (1978)
ISRM: Suggested methods for determining the uniaxial compressive strength and deformability of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. & Geomech. Abstracts 16(2), 138–14 (1979)
Karakus, M.; Kumral, M.; Kilic, O.: Predicting elastic properties of intact rocks from index tests using multiple regression modeling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 42, 323–330 (2005)
Sabatakakis, N.; Koukis, G.; Tsiambaos, G.; Papanakli, S.: Index properties and strength variation controlled by microstructure for sedimentary rocks. Eng. Geol. 97, 80–90 (2008)
Soroush, H.; Qutob, H.: Evaluation of Rock Properties Using Ultrasonic Pulse Technique and Correlating Static to Dynamic Elastic Constants,” The 2nd South Asain Geoscience Conference and Exhibition, GEO India, New Delhi (2011)
Kern, H.: P and S wave anisotropy and shear-wave splitting at pressure and temperature in possible mantle rocks and their relation to the rock fabric. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 78(3–4), 245–256 (1993)
Karpuz, C.; Pa-Samehmetoglu, A.G.: Field characterization of weathered Ankara andesites. Eng. Geol. 46(1), 1–17 (1997)
Fener, M.: The effect of rock sample dimension on the P-wave velocity. J. Nondestr. Eval. 30(2), 99–105 (2011)
Ercikdi, B.; Karaman, K.; Cihangir, F.; Yılmaz, T.; Aliyazıcıoglu, S.; Kesimal, A.: Core size effect on the dry and saturated ultrasonic pulse velocity of limestone samples. Ultrasonics 72, 143–149 (2016)
Sonmez, H.; Tuncay, E.; Gokceoglu, C.: Models to predict the uniaxial compressive strength and the modulus of elasticity for Ankara agglomerate. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 41(5), 717–729 (2004)
Monjezi, M.; Khoshalan, H.A.; Razifard, M.: A neuro-genetic network for predicting uniaxial compressive strength of rocks. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 30(4), 1053–1062 (2012)
Shahri, A.A.; Larsson, S.; Johansson, F.: CPT-SPT correlations using artificial neural network approach- A case study in Sweden. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 20(28), 13439–13460 (2015)
Shahri, A.A.: Assessment and prediction of liquefaction potential using different artificial neural network models: a case study. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 34(3), 807–815 (2016)
Shahri, A.A.; Asheghi, R.: Optimized developed artificial neural network-based models to predict the blast-induced ground vibration. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-018-0137-4
Esmaeilabadi, R.; Shahri, A.A.: Prediction of site response spectrum under earthquake vibration using an optimized developed artificial neural network model. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 10(30), 76–83 (2016)
Hornby, G.S.: ALPS: The Age Layered Population Structure for Reducing the Problem of Premature Convergence. Proceedings of the 8th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation (GECCO '06). July 2006 pp:815–822 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1145/1143997.1144142
Hornby, G.S.: Steady-state ALPS for real-valued problems. Proceedings of the 11th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation (GECCO '09). July 2009 pp: 795–802 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1145/1569901.1570011
Hornby, G.S.: A Steady-State Version of the Age-Layered Population Structure EA. In: Riolo R., O'Reilly UM., McConaghy T. (eds) Genetic Programming Theory and Practice VII. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. Springer, Boston, MA. (2010) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1626-6_6
Lim, T.Y.: Structured population genetic algorithms: a literature survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 41, 385–399 (2014)
Patnaik, A.K.; Agarwal, L.A.; Panda, M.; Bhuyan, P.K.: Entry capacity modelling of signalized roundabouts under heterogeneous traffic conditions. Transp. Lett. 12(2), 100–112 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özdemir, E. A New Predictive Model for Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Rock Using Machine Learning Method: Artificial Intelligence-Based Age-Layered Population Structure Genetic Programming (ALPS-GP). Arab J Sci Eng 47, 629–639 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05761-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05761-x